Sorry that I missed our daily confab yesterday, campers. I got a new pair of eyeglasses the other day, with spiffy cutting-edge lenses that optometrist and optician alike assure me will be the optical standard ten years hence, and my eyes have been rather baffled by them. Headaches, blurriness, the works. I’m told that these minor side effects (such as NOT BEING ABLE TO SEE WELL) will pass off in a few days, as my eyes become used to the space-age materials currently before them, but on the whole, I thought it would be better if I did not share my thoughts with you fine people while I could not confirm that what I thought I was typing was actually what was appearing on the screen.
Hey, no one is that good a touch-typist.
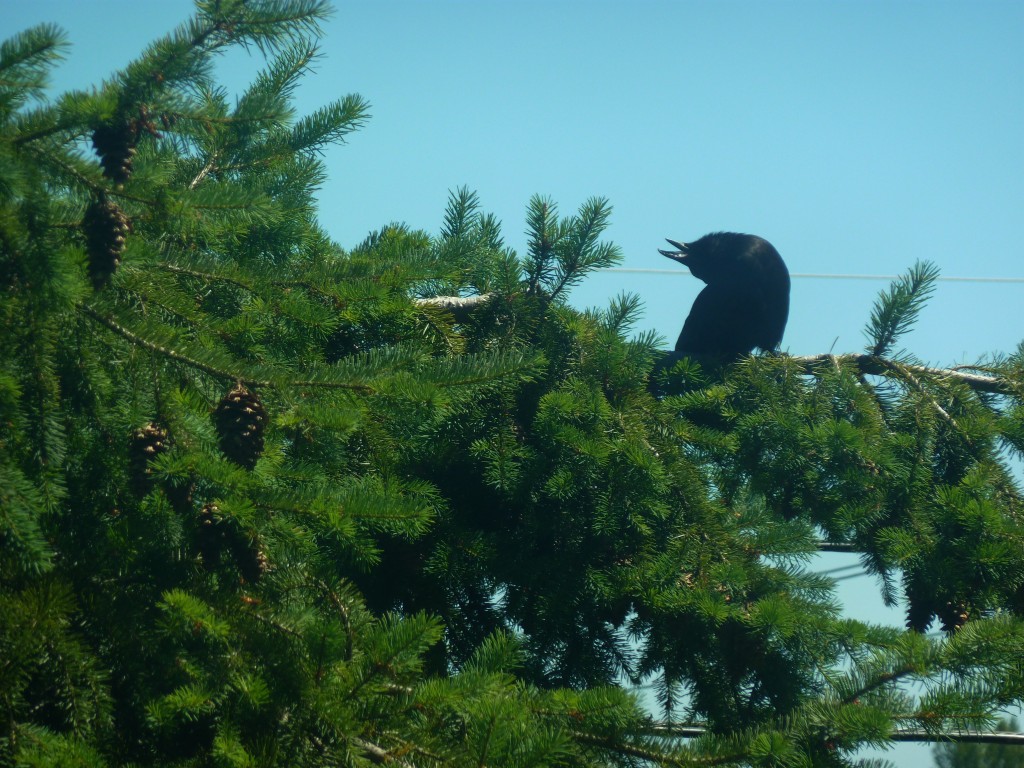
Speaking of one’s eyes playing tricks on one, no, yours are not: the photo above does indeed depict a crow bending over backwards, for reasons best known to itself. When I first spotted him outside my studio window, I feared he had a broken neck. Ten minutes later, however, he startled me horribly by switching to this dignified pose:

Followed closely by this equally majestic stance:
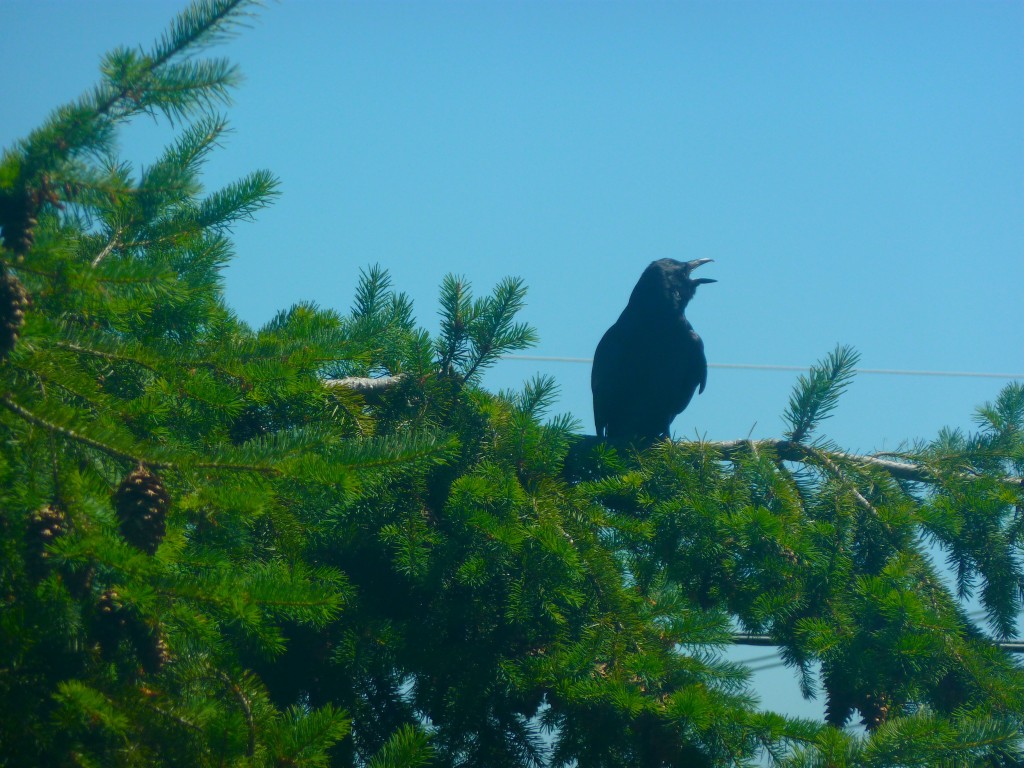

He seemed to find this last position quite comfortable: he remained like that for the better part of an hour, squawking irritably at passing birds, presumably because they did not spontaneously drop food into his waiting gullet. Had he been a small bird, of a size and shape one might expect from a fledgling recently tumbled from a nearby nest, this behavior might have made more sense, but our hero was immense, a titan among crows.
He should, in short, have known better. And so should protagonists who go around asking other characters questions.
That’s right, campers. It’s time once again for my annual foray into concentrate upon one of my all-time favorite species of expendable text: the kind of dialogue that results from a protagonist’s being a really, really poor interviewer.
Oh, don’t roll your eyes; this is a serious manuscript megaproblem. A protagonist who doesn’t ask good questions — or necessary follow-up questions — can slow a novel, memoir, or creative nonfiction book to a limping crawl.
Why does it matter how skilled a questioner the protagonist is, you ask, unless s/he is a journalist of some sort? Simple: many, many, MANY novel plots require their protagonists to learn something that they do not already know — and, more importantly, that the reader does not already know. Who killed the Earl of Cheswick, for instance, or why so many people are interested in that darned ugly Maltese Falcon.
Don’t heave a sigh of relief, writers of anything but mystery or suspense. Most fiction plots feature at least one interview scene, regardless of book category. Let’s face it, few human beings currently treading the earth’s crust are omniscient; as a result, an extremely high percentage of plots involve the protagonist(s) trying to find something out. Why does everyone in town refuse to talk about the day the old mill burned down? Why does Uncle Mortimer limp? Why is the boss suddenly acting so standoffish? What’s in that casserole, anyway? Why don’t you love me like you used to do, when my hair’s still curly and my eyes are still blue?
Getting the picture?
In the pursuit of answers to these and other burning questions, the protagonist is, necessarily, frequently forced into the role of interviewer, trying to extract information from other characters. What a pity, then, that protagonists have a nasty habit of slowing down the collective search for truth by neglecting to promising lines of questioning, failing to follow up on something just said, or just plain being too polite to ask the questions the reader is dying to ask herself, but can’t.
The result? A protagonist standing there with his beak open, waiting for some passerby to drop something yummy into it.
The last time I wrote about this particular manuscript megaproblem, as so often happens when I have planned to attack a particular issue, craft or promotional, in this venue, the Fates trundled up with a wheelbarrow and dumped an excellent example right at my feet, the kind of real-life incident that novelists and memoirists alike love to incorporate into their narratives. It would have been ungrateful of me not to use it as an example, right?
Heaven forfend that we should disregard the gift of the Fates. See if you can catch the interviewing problem in the following story. To render it a trifle more instructive, I shall present it in standard manuscript format — and as usual, if you should have difficulty making out the words, try enlarging the image by holding down the COMMAND key and pressing +.


Okay, what did you identify as the problem here? If you pointed out the extremely common one of an actual event’s being substantially funnier to live through than to read, give yourself a gold star for the day. If, on the other hand, it occurred to you that I told the story, as so many recorders of real life do, as if any reader’s reactions would have been identical to mine in the moment, award yourself another.
Memoirs and fictionalized reality frequently suffer from both of these defects. And why? Haul out your hymnals and sing along with me, campers: just because something actually happened does not mean that it will be interesting, amusing, or even worth recording on the page.
But these were not the only weaknesses you spotted in this narrative, were they? If you blurted out something about my having told what happened, instead of showing it — an interpretive dance could cover a lot of different types of action, right? — be mighty pleased with yourself. If you said that I was attributing thoughts to Pansy that the first-person narrator of this piece could not possibly have heard without being as clairaudient as Joan of Arc, pat yourself on the back yet again.
Good job. Now — what would be the single easiest way to revise this scene to render it more engaging to the reader? That’s right: by making the narrator a better interviewer.
Had I asked more insightful questions of either myself (why did the song disturb me so much? Did it have something to do with the time I heard an entire van full of 11-year-olds sing Madonna’s “Like a Virgin” at the top of their lungs on my first day as an after school program volunteer all those years ago?) or of Pansy (did she realize that adults associate that particular kind of music with something she’s not supposed to know about for years to come, or had she simply heard in on a commercial? Was she trying to provoke a specific reaction in me, her uncle, the gerbil?), I could have rendered the situation more dramatic while simultaneously doing more character development. Had I written the dialogue with an eye to increasing conflict, I might even have avoided that hackneyed scene ender that we’ve all seen so often in TV shows and movies, the protagonist’s running out of the situation in order to avoid conflict that would have been interesting on the page.
Some of you are just dying to register an objection, aren’t you? “But wait — you were reproducing real-life dialogue,” all of you would-be objectors point out. “Wouldn’t it be less realistic if you changed it?”
In a word, no. In several words, not if I write the scene well.
As I’ve observed many times before and shall no doubt again, just because something actually happened doesn’t mean it will automatically read realistically on the page. It’s the writer’s job to craft dialogue — or any scene, for that matter — so it’s plausible, not the reader’s to make allowances because the writer observed someone saying or doing what ended up on the page. Besides, real-life dialogue is often dull.
That’s especially true in interview scenes, incidentally: few standard narrative devices annoy professional readers (like agents, editors, contest judges, and our old pal, Millicent the agency screener) who’ve been at it for a while than a narrator — or protagonist — who is a lousy interviewer.
Why? Well, for starters, lousy interviewers are so very common in submissions. On a manuscript’s page, a poor interview scene tends to run a little something like this:
“I swear,” Romeo claimed, one hand over his heart and the other hovering over the graying head of his sainted mother, “that’s all I know. Please don’t ask me any more questions.”
Juliet drummed her long piano-player’s fingers on the rich mahogany tabletop. Her every instinct told her that he was not telling the truth — or at least not the whole truth. The very fate of Western civilization rested upon her solving this puzzle before midnight tomorrow, and this one well-protected, diamond-encrusted lady obviously held the key.
She stood and offered her hand to the old woman. “Charming to meet you, Mrs. Montague. You must come to my house for brunch sometime. I hate to boast, but I make extraordinary deviled eggs.”
Romeo detached their clasped hands so quickly that Juliet’s hand burned. “Must you go so soon? Here’s your coat — I’ll walk you down to the cab stand on the corner before I release the vicious dogs that prowl our estate at night to discourage post-midnight visitors.”
Juliet fumed, but what could she do? “Goodbye,” she called back from the hallway.
“Don’t forget to sprinkle your eggs with paprika,” she could hear Mrs. Montague bellowing after her. “I love paprika.”
Why might an exchange like this prove annoying to a professional reader? For the same reasons that my anecdote about Pansy might strike ‘em as underdeveloped: because a poor interview scene represents a lost opportunity for intriguing conflict — rich potential for drama presented then abandoned by the narrative for no apparent reason.
Okay, so that’s not quite fair: writers often have what they consider pretty strong reasons for rushing their protagonists away from conflict. Trying to make them more likeable to the reader by demonstrating common courtesy, for instance, or forcing them to work harder to learn the Awful Truth.
Or wanting to stretch the novel from 100 pages to 200. My point is, regardless of the motive, this practice tends to render those of us who read manuscripts for a living a tad impatient.
Why? Well, think about it: in a first-person or tight third-person narrative, the protagonist is the reader’s surrogate in ferreting out information; as a reader, it’s not as though I can jump into the storyline, grab a microphone and tape recorder, and start grilling the usual suspects. After a while, an inept interviewer can start to annoy the reader simply by being a poor tour guide to the plot.
I sense some uncomfortable squirming out there, don’t I? “But Anne,” I hear some of you suspense-lovers cry, “a too-good interview could give the entire plot away! What about building tension?”
You have a fine point, suspense-mongers: revealing the truth in slow increments is one way to create suspense. It’s such a fine point that I’m going to spend most of the rest of the post talking about how to do just that.
Before I do, however, allow me to observe that making information unavailable through the simple expedient of not having the protagonist ask anyone about it for 200 pages tends to fall very, very flat with readers. And not only professional ones like Millicent, who tend to harbor a well-founded objection to narratives that toy with them too much.
Why might a lay reader object, you ask? Well, while readers do like to second-guess what’s going to happen next, trust me, it’s going to make your protagonist substantially less likeable if the reader keeps thinking, “Ask about the elephant in the room, you fool! Don’t just walk away!”
A professional reader — such as an agent, editor, contest judge, Millicent, or yours truly — is likely to react with even less sympathy, because a disproportionate percentage of submitted manuscripts create suspense by deliberately withholding information from the reader.
Especially if that information happens to be something that the protagonist already knows. We pros like to call this creating false suspense.
The most famous example, of course, is the sleuth from whose perspective the reader has viewed the entire case suddenly stops communicating his thoughts on the page — then gathers all of the still-living characters in the nearest drawing room (there always seems to be one handy, doesn’t there?) and announces, “You may be wondering why I asked you all here…”
Darned right we’re wondering — the reader wants to know why you suddenly withdrew your confidence from him, Mssr. Poirot.
Again, don’t start feeling too smug, those of you who write something other than mysteries — protagonists’ playing interviewer role is hardly limited to that genre. If you have ever constructed a narrative that involved dialogue, you’ve almost certainly written at least one interview scene.
What makes me so darned sure of that? It’s rare that any novel — or, indeed, any book with a plotline — does not contain a one scene where somebody is trying to extract unknown facts from someone else. Queries ranging from “Does that cute boy in my homeroom REALLY like me, Peggy?” to “Where did the cattle go, Tex?” aren’t just dialogue filler — typically, they call for character-developing and/or plot-satisfying responses.
In fact, it’s a fair bet that any scene that contains one character exclaiming, “What happened?” is the precursor to an in-text interview.
Are those of you who have survived previous craft series with me already warming up your highlighting pens, in anticipation of my ordering you to aim them at the interview scenes in your work? Good idea. Such scenes often beg to be flagged for revision, because they are so very hard to pace well.
Yes, even when the information being revealed is inherently exciting (“If you do not cross the bridge before sunset, giant bats will eat you, Evelyn.”), emotionally revealing (“The reason I turned to piracy is — YOU, Father!”), or just plain necessary to make the plot work (“Yes, Herbert, although I haven’t seen fit to mention it once in the course of our sixty-two-year marriage, I have always dreamed of going spelunking!”).
Why might presenting any of these plot points present pacing problems? (Try saying that seven times fast!) Well, when the point of a scene is for information to be revealed to the protagonist (and thus the reader), many writers become so focused upon that data’s being revealed entertainingly that they run to the opposite end of the reticence spectrum and have characters (secondary ones, usually) blurt out the necessary information practically BEFORE the protagonist asks for it.
This, too, is an interviewing problem — and one of the greatest sappers of narrative tension the world has ever known.
Many, many submissions where secrets that have been kept successfully for 25 years burst out of the mouths of the secretive practically the moment that the protagonist walks into the room. So why, the reader is left to wonder, if these secret-keepers are so willing to spill their guts to the first person to ask a direct question, has this information not been revealed before?
The apparent answer: because the plot required that it not be revealed before. And that, my friends, is never a sufficient motivation from the reader’s point of view. Or Millicent’s.
To be blunt about it, too-easy detective work makes the mystery seem less important. It’s hard to care much about a secret if the narrative makes it evident that the hidden information would have been laughably easy to get all along, if only someone had thought to knock on the door of the only person who actually observed that the setting of that fire a decade before that shaped the entire town’s subsequent history.
You can just imagine all of the townsfolk slapping their heads in unison behind closed doors after that perky newcomer digs up the arsonist’s name in a single afternoon: “Why oh why didn’t it occur to any of us to ask Aunt Bessie why her nephew kept the garage stuffed to the rafters with matches? How could we have missed so self-evident a clue?”
I can answer that, perplexed villagers: because the author didn’t want you to solve the mystery before her protagonist arrived on the scene.
Astonishingly often, the protagonist doesn’t even need to ask a question to elicit the revelations of tremendous secrets from minor-but-essential characters. Often, all she has to do is show up, and the legendary recalcitrant loner begins singing like a Rhine maiden: “So, Mr. Bond, now that I have you tied to that chainsaw, it’s time for me to reveal my evil plan…”
Or, as our friend the crow might put it: where’s my breakfast?
In many instances, the protagonist is reduced to helpful nods and murmured promptings on the order of, “Oh, really?” while the imparter engages in a soliloquy so long that Hamlet himself would start looking at his watch four paragraphs into it.
Yet a novel, the last time I checked, was not an opera: in real life, most people do not go around shouting out their deepest, darkest secrets at the top of their lungs to relative strangers. Yet when was the last time you heard an advocate of realism on the page object to the formerly mild-mannered librarian suddenly bursting into florid epic storytelling mode the instant a protagonist asks for a particular book?
What makes secrets interesting, generally speaking, is the fact that not everyone knows them. Good mysteries are hard to solve; intriguing truths are hard to dig up. In real life, it is actually rather difficult to convince folks to cough up the truth — partially because after one has lived with a lie long enough, one often starts to believe it oneself.
How’s that for an intriguing narrative possibility?
When you are trying to increase the overall level of tension throughout a novel, recognizing that truth is often difficult to elicit is a powerful tool, one that can revolutionize how you handle interview scenes. They do not need to be essentially one-sided information dumps they so often are. Instead of regarding them as just necessary exposition-through-dialogue, to be rushed through quickly, why not use the opportunity to introduce some conflict?
Or heck, if you really want to get adventurous, some character development?
How does one pull that off? Actually, there’s a pretty simple revision trick: try making the information-imparter more reluctant to cough up the goods.
This both forces the protagonist to become a better interviewer and renders the information-seeking process more difficult. Automatically, this small switch will render the scene more interesting, by introducing viable (if brief) conflict between Character A (who wants to learn something) and Character B (who has very good reasons not to pass on the information).
Yes, this will probably make the scene longer, but remember, the role of a hidden truth in any narrative is not to be solved as quickly as possibly, but as enjoyably for the reader as possible. Not to mention — and this isn’t an insignificant consideration when trying to get a submission past Millicent to her boss, the agent of your dreams — being less like the kind of clichéd interview scenes we’ve all so often seen in TV cop dramas, where the most common interview techniques consists of:
(a) asking the suspected criminal/accomplice/victim-who-turns-out-to-be-in-on-it direct questions,
(b) instead of asking follow-up questions, threatening him/her/the accomplice if the interviewee doesn’t instantly blurt out what the interviewer wants to know (what used to be known in old pulp mysteries as “singing like a canary”),
(c) if no blurting occurs, the interviewer’s stomping off in a huff to pursue other clues, thus prematurely ending a potentially interesting conflict.
Yes, there are probably real-life police officers who interview this way, but I can’t believe that they’re very good at their jobs. And even if they are, would reproducing this kind of dialogue in every interview situation be compelling in a book? Probably not.
Again, perish the thought that this basic principle applies only to mysteries. Let’s take a look at the interviewing strategy my narrator took vis-à-vis young Pansy:
(a) Auntie asks Pansy where she learned that, um, charming little ditty.
(b) Upon not receiving an adequate explanation, Auntie does not ask follow-up questions, but instead
(c) scurries off, embarrassed, to score some cupcakes, thus prematurely ending a potentially interesting conflict.
In real life, of course, it’s not all that surprising that someone might side-step the particular conflict in this anecdote. I’m not, after all, one of the girl’s parents; I have no idea how they might or might not have explained the musical scoring choices of adult filmmakers to their offspring. (Or at any rate I didn’t know at the time; I’ve since mentioned the incident to Pansy’s mom, to minimize the possibility that the child’s next bravura performance of that musical number will take place in school, where she might get into some real trouble. Or in church.) As a protagonist in a novel or memoir, however, slinking away from conflict just because it might prove uncomfortable is about the most boring choice I could have made.
Come on: you wouldn’t have liked that story to end with my telling you how and where Pansy learned the song? Or that you wouldn’t have liked me — in the story, at least — to have asked some follow-up questions? Or that as a reader, it doesn’t annoy you just a little bit to know that I did in fact learn the answer, but I’m just not telling you what it was?
Starting to empathize more with Millicent’s impatience when she sees this sort of interview scene in fourteen consecutive submissions in any given week? And she’s not the only one who is notoriously touchy about it: ineffectual interviewing and false suspense are both legitimately annoying narrative practices.
Take a page from the time-honored pirate’s manual: make your treasures hard to dig up, and don’t have your protagonist walk away from potentially interesting interview subjects at the first sign of resistance. The more difficult it is for your protagonist to ferret out the truth, the more engaged the reader will be in the search process.
Or, to put it another way: go forage for yourself, Mr. Crow.
How might a savvy reviser take this principle to heart? Consider eschewing the magic wand that turns the timid secretary who saw her boss murdered 15 years ago and ran off to live in a cave to avoid talking to the police into the operatic diva belting out precisely the information she has devoted to her life to hiding, simply because someone finally asked her a direct question about it. Banish the clue that only required someone opening the right cupboard drawer to find. Give your protagonist some killer interview skills — and give your interview subjects stronger backbones.
Your manuscripts will be more interesting for it, I promise. Keep up the good work!