For the last week and a half, I’ve been going over a real, live manuscript with the same variety of fine-toothed comb that Millicent the agency screener, Maury the editorial assistant, and Mehitabel the veteran contest judge so frequently pass around amongst themselves. While the experience of seeing just how closely professional readers scan manuscripts can be quite scarifying for a writer new to the game, just being aware that no gaffe, however small, is likely to pass unnoticed under Millicent’s watchful gaze can render that poor, trembling, crestfallen writer a significantly better reviser for the rest of his writing life: never again will he assume, as the vast majority of aspiring writers seem to do, that pretty good is close enough where submissions are concerned.
Or, to put it another way: perfect formatting, impeccable spelling and grammar, and a flowing, likable narrative voice are the minimum requirements for Millicent, Maury, and Mehitabel to admire a manuscript, and a legitimately gripping hook, an interesting protagonist(s), and an intriguingly conflict-ridden plot are generally necessary to keep them reading beyond page 1.
This is hardly a well-kept secret, right, accessible only to those brave enough to climb to the top of Manhattan’s tallest building, turn around three times, and sacrifice 17 first editions of PEYTON PLACE on a bonfire to the literary powers that be? In these days of easy Internet access and free dissemination of information, an aspiring writer could hardly make it through the first 20 entries of a web search under getting published without learning that the competition is so fierce for agents these days that the average Millicent sees hundreds of technically perfect submissions in any given year.
Yet most aspiring writers submit manuscripts that fall short in one or more of these areas — and then are astonished when their work is rejected. Whether they admit it openly or not, they had been operating on the presumption that if the writing were stylish enough and/or the story intriguing enough, professional readers everywhere would be perfectly willing to overlook every other manuscript problem.
In fact, most aspiring writers are downright indignant when they first learn that this is not the case. I hate to be the one to break it to you (although that’s never stopped me before, has it?), but to Millicent and her ilk, technically flawless presentation of writing is simply a quality of professionalism, not the ultimate goal of a collaborative editorial process that happens mostly after a writer lands an agent.
Have I convinced you yet that proofreading before submission might be a prudent notion? Think about it: how are you ever going to know for sure how stylistically strong your writing is until it is free of distracting gaffes?
How distracting are those so-called little things, from a professional reader’s perspective? Let’s take a peek at what might happen if the first page of one of the great classics English literature if it happened to land on Millicent’s desk before she’s had her second cup of coffee?

See? Even a great story well told could use a little presentation help. Or at least a touch of updating: norms of literary style vary over time, like any other aesthetic trend.
I wanted to bring that up, on the off chance that any of you should be trying to land an agent for an aggressively 19th-century style novel. Or in case anyone had been casting about for a comeback for the next time that guy standing next to you at that bar that’s never more than 100 yards from any writers’ conference in North America starts griping about how the publishing world isn’t really interested in literature anymore. Why else, he reasons, could anyone possibly have rejected his manuscript?
Even without reading it, I would be willing to hazard a guess: the little things. And probably not just one or two of ‘em, either.
What makes me so sure of that? Well, experience: although submissions get rejected all the time for what most writers would consider nit-picky reasons, it’s virtually unheard-of for any manuscript to have only one problem. As we like to say here at Author! Author! — like ants, writing problems seldom travel alone.
That’s vital for a submitting writer to understand, particularly in these decadent days, when even entire manuscripts are frequently rejected with no explanation at all — or, still worse but increasingly common, rejected without even so much as a form letter notifying the writer. Because it’s so easy to guess wrong when casting about for a rationale, I would STRONGLY caution any aspiring writer against leaping to the conclusion that any single problem, formatting or otherwise, was the only reason a manuscript was getting rejected. As we have seen in recent posts, Millicent’s decision to reject is often based upon quite a few reasons working in tandem.
Which is why, unfortunately, it’s not all that uncommon for your garden-variety Millicent, Maury, or even Mehitabel to come to believe that an improperly-formatted manuscript, or one containing a few misspellings, will inevitably turn out to be poorly-written overall. In their experience, it’s unlikely to the point of laughability that changing only one thing, even a major one, in the average manuscript would render it rejection-proof.
There is no such thing as a rejection-proof manuscript, you know. While it would indeed be delightful if there were a magical formula that could be applied to any manuscript to render it pleasing to every Millicent currently screening manuscripts, that formula simply doesn’t exist; individual tastes and market trends vary too much. Not to mention the fact that the slow economy is making most agents and editors really, really cautious about picking up any first manuscript at all right now.
Even, alas, very clean ones, free of formatting problems and grammatical mistakes. At the moment, no first-time author is getting a free ride. But you can bet your boots that the ones that are getting picked up are being selected from amongst the cleaner manuscripts.
But clean doesn’t mean devoid of individual style, right? Right? Do stop erasing adverbs from your tag lines long enough to answer me.
It’s most helpful, I’ve found, to think of revising your manuscript as clarifying your style, rather than forcing your story and voice into some mythical conception of perfect writing, the color of which Millicent happens to be thinking while she’s screening manuscripts. Like standard format, manuscript cleanliness is not a magic wand that can be waved over a submission to make every agent, editor, and contest judge on the face of the earth squeal with delight at the very sight of it.
It’s merely is a means of presenting your writing professionally, so Millicent, Maury, and Mehitabel will be able to weigh it on its non-technical merits.
Or, to put it another way: taking the time to clean up your manuscript will make it less likely that your submission will be rejected on a knee-jerk basis. But it’s just a fact of publishing even a perfectly clean manuscript is going to garner its share of rejections, if it’s sent out enough.
So what should a savvy submitter be editing toward, over and above minimizing the more notorious of Millicent’s pet peeves? Come closer, and I’ll let you in on a secret of good writing: it flows smoothly. A compelling narrative voice is a consistent one.
Pulling that off is a lot harder than it sounds, you know; a seamless narrative is virtually always the result of many, many careful attempts at revision. The more successful those attempts, the less labored the result will seem — and the more writers brand-new to the writing game will derive the quite mistaken impression that their favorite books were their respective authors’ first drafts, and thus (they assume) that their own first drafts should be marketable without further revision.
That’s an unfortunate misconception, because the author of a well-crafted narrative works hard to create the illusion of spontaneous consistency. Awfully hard. Seamlessness doesn’t happen by accident, you know.
I blame the stubbornly pervasive real talent = first draft so good it needs no tweaking myth for the fact that many aspiring writers become quite testy when even manuscript faults easily discovered in a quick proofreading are pointed out to them. “Oh, the little stuff doesn’t matter,” they insist when some kind soul takes it upon herself to explain that the period belongs within the quotation marks, not after them, or that while a .75 inch bottom margin may well shrink the length of an overlong manuscript, Millicent is quite likely to see through the ruse. “The technical problems can be cleaned up later. All a good agent (editor, contest judge) will really care about is a good story well told.”
Had that ever actually been the case in publishing history — and offhand, I can’t think of a period when these were the only criteria for getting published — a good ten percent of the manuscripts Millicent sees every year would get snapped up immediately. The author would provide the story and the overall voice, and some luckless soul confined to the bowels of the publishing house would be assigned to excise all of the misspellings, grammatical problems, logic problems, continuity problems, storytelling problems, and all other text-based snafus prior to publication.
All the author would have to do is cash the royalty checks and show up to the occasional book-signing. Unfortunately, the publishing world doesn’t work like that.
In the first place, the average agent is not in a position to pick up the 10% of submissions that are well-written — or even her 10 favorite manuscripts of the year, usually. In the current literary market, most agents are picking up just a few clients per year. Given the choice between signing a client who produces impeccably-edited manuscripts and one whose work needs extensive revision, which would you choose?
Or, to put it another way: had you considered applying to medical school instead of trying to land an agent? Your chances of getting accepted are quite a bit higher.
In the second place, as publishing profits have dropped lower and lower — and it was not all that profitable a business to begin with — fewer and fewer people are charged with shepherding a manuscript from acquisition to publication. It’s a rare editor who has the time to proofread, much less the inclination. Consequently, the value of a writer who can (and does) produce beautifully-edited pages all on her own grows greater with each passing day.
Or, to put it another way: expect to be 100% responsible for copyediting your own work — and for book promotion as well, most likely. Your editor will probably make general revision suggestions, but bringing the finished manuscript up to professional standards is ultimately going to be up to you.
I’m not bringing all of this up merely to depress you, contrary to what 2/3rds of you had been thinking very loudly indeed throughout the last few paragraphs — although frankly, given how radically speakers at most writers’ conferences soft-pedal these realities, I suspect a little well-timed depression-inducement might keep a lot of aspiring writers from assuming that the only possible reason that their work hasn’t landed them an agent is the writing quality. I’m bringing it up so writers may begin to come to terms with the reality that revising your writing is not extraneous to the writing life; it’s an integral requirement of it.
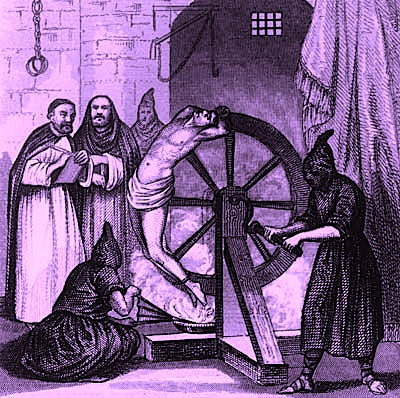
And when I say revising, I mean reworking your pages under the assumption that your target reader’s eye is as critical as this:

Or, to put it another way (and if the repetition of that phrase automatically made your teeth grind this time, congratulations; you’re starting to read like a professional): it’s in your competitive interest to assume an uncharitable first reader. This places the onus for presenting your writing in its best light squarely where it should be: on you, the writer.
Yet even as I typed that last paragraph, I could feel all of this excellent (if I do say so myself) advice bouncing off the heedless many who simply submit whatever opening pages they happen to have saved on their hard disks at the moment an agent requests materials, even if those pages haven’t even been proofread or spell-checked yet. Yes, well-meant guidance ricochets straight off those people, landing instead upon the already beleaguered heads of compulsive revisers everywhere.
You know who you are: you’re the ones who gasp every time I start a new series of revision tips, scurry toward your manuscripts, and stay up half the night revising. You not only spell-check and proofread — you’ve stared at individual scraps of dialogue so long that you are no longer sure anymore whether the dialogue makes sense. You grind your teeth over battle scenes, wondering if there’s enough conflict on each page. And three days after you have submitted requested materials to an agent, you find yourself compulsively reading over your submission, searching for flaws that could scuttle your chances of making it past Millicent.
In short, you’re just like most working authors, bless your perfection-seeking hearts. We’re a worry-prone breed.
While that worry can be an outright blessing over the course of a book-long revision — what, stop halfway through Chapter 17, when there are 8 more chapters to go? — it can be something of a curse when trying to get requested materials out the door in a hurry. All too often, what chronic revisers end up sending is an uneven draft, hovering somewhere between Revision #12 and Revision #23.
How does that happen? Well, page 1 made it all the way through Revision #23, but at the time the agent of your dreams requested those first 50 pages, page 2 was still in the throes of an incomplete #17. Pages 3-10 are mostly the same as they were way back in #4, while Chapter Two is entirely new as of a week ago.
Getting the picture? The urge toward conscientious, ongoing revision — that drive for constant textual improvement that any agent in her right mind would be overjoyed to find in a new client — can often result in a submission that looks at first glance, ironically, as though it hasn’t been revised at all.
I know: bummer. I like to call it the Frankenstein manuscript phenomenon. Like Frankenstein’s monster, it’s made up of a part from here, a part from there…
Why is that a submission problem, you ask? Again, to put it another way: what do you think Millicent, Maury, or Mehitabel thinks when they encounter, say, one sentence that’s in the past tense, followed by three that are in the present, because the phone happened to ring while the writer was in mid-revision? Or a character is named George on page 8 and Jorge on page 127, because the writer just didn’t have time to implement a late-breaking name change all the way through the manuscript?
Or even a problem as subtle as the unintentional perspective shift that follows, because Junior accidentally caught Sissy’s braids in the blender an hour and ten minutes after Mom realized with a shock that the story she had almost finished drafting with an omniscient narrator would work much better as a tight third-person piece focused solely upon the protagonist?
Great heavens, Edna thought irritably, isn’t anything going to go right today? First, the apple pies burned because she stayed too long on the phone with Mom, listening to her complain about her lumbago (what is that, anyway?), then it was so hot in the American Legion lodge’s kitchen that all of her carefully-applied make-up had melted right off her face and down onto her seersucker collar. Jeremy White had been so startled by her appearance when he bumped into her in the corridor that he had to bite the inside of his cheek to keep from screaming aloud. She couldn’t possibly serve the veterans while sporting runny eyeliner, could she?
You wouldn’t have caught it if you hadn’t been looking for it, would you? (And in case you didn’t catch it: in three of the four sentences, the perspective remains squarely with Edna; in sentence #3, the reader is treated to what’s going on inside Jeremy’s head. Perfectly proper in an omniscient narrative, of course, but out of bounds in the tight third person with a single protagonist.)
Sometimes, the monster’s ways are subtle, as you may see, and sometimes blatant. However he may choose to manifest in the submission at hand, I must repeat my earlier question: what, I ask you, would a professional reader’s response be to any of these perfectly explicable clashes of incomplete revision passes?
“Inconsistency,” Millicent, Maury, or Mehitabel breathe in unison. “This manuscript needs more work.”
Or at least (if I may be permitted to chime in here) a good authorial read-through IN ITS ENTIRETY, IN HARD COPY, and OUT LOUD.
So here, my dear chronic revisers, is a revision series aimed squarely at you. For the next week or so, we’re going to be talking about how to transform that Frankenstein manuscript into a submission that positively glows with professionalism.
And you thought I wasn’t going to give you a Memorial Day present! Keep up the good work!
PS: speaking of Memorial Day, why not spend a few minutes this weekend sending in an entry to the Author! Author!/WHISPER Great First Page Made Even Better Contest? The deadline is this coming Monday at midnight in your time zone. Fortunate entrants will win hard-nosed professional critique of their opening pages BEFORE submitting them to Millicent, Maury, or Mehitabel!