Hello, campers –
Today, I’m giving us all a much-deserved respite from our rather taxing ongoing series on conference pitching to bring you all a reward for virtue — no, make that several rewards for virtue. Remember earlier this summer, when award-winning police procedural author and fab guy Stanley Trollip stopped by to give us his insights on publication contracts, promising to return to tell us all about his book tour for his second novel, THE SECOND DEATH OF GOODLUCK TINUBU?
Well, jump for joy, fans of thrillers and book signings: he has proven as good as his word.
For those of you who have joined the Author! Author! community only recently, Stan is best known as Michael Stanley, nom de plume of Stan Trollip and Michael Sears. It’s one of the great thriller collaborations of our time.
But don’t take my word for that: the Los Angeles Times named their last novel, A CARRION DEATH, as one of the top ten crime novels of 2008. It also raked in finalist honors for the Minnesota Book Award, Strand Magazine’s Critics Award for Best First Novel, and Mystery Readers International Macavity Award for Best First Novel.
The flattering buzz has been even louder for their new novel, THE SECOND DEATH OF GOODLUCK TINUBU. Here’s the publisher’s blurb for it, along with both the US cover and the cover and title you’d see if you happened to be browsing in a Canadian or UK-based bookstore:
How can a man die twice?
That is the question facing Detective David “Kubu” Bengu when a mutilated body is found at a tourist camp in Northern Botswana. The corpse of Goodluck Tinubu displays the classic signs of a revenge killing. But when his fingerprints are analyzed, Kubu makes a shocking discovery: Tinubu is already dead. He was slain in the Rhodesian war thirty years earlier.
Kubu quickly realizes that nothing at the camp is as it seems. As the guests are picked off one by one, time to stop the murderer is running out. With rumors of horrifying war crimes, the scent of a drug-smuggling trail, and mounting pressure from his superiors to contend with, Kubu doesn’t notice there is one door still left unguarded – his own. And as he sets a trap to find the criminals, the hunters are closing on him…
Not a bad pitch, is it? Notice how those one-of-a-kind details just leap out at you? Out comes the broken record again: never, ever forget that even the most tedious chore in book description is an opportunity to show what a good storyteller you are.
I digress, however. I promised you goodies, and goodies you shall have.
A whole literary cornucopia of them, too: to keep things interesting, not only will Author! Author! be bringing you Stan’s insights today, but a newfangled high-tech treat and a good, old-fashioned contest. To avoid scaring any technophobes out there away from winning a copy of THE SECOND DEATH OF GOODLUCK TINUBU free, gratis, and entirely without encumbering your monetary worth even tangentially, allow me to fill you in about the contest first.
To prepare you to enter, please study this lovely photo of precisely the kind of literary event most aspiring writers would happily give their little toes to attend:
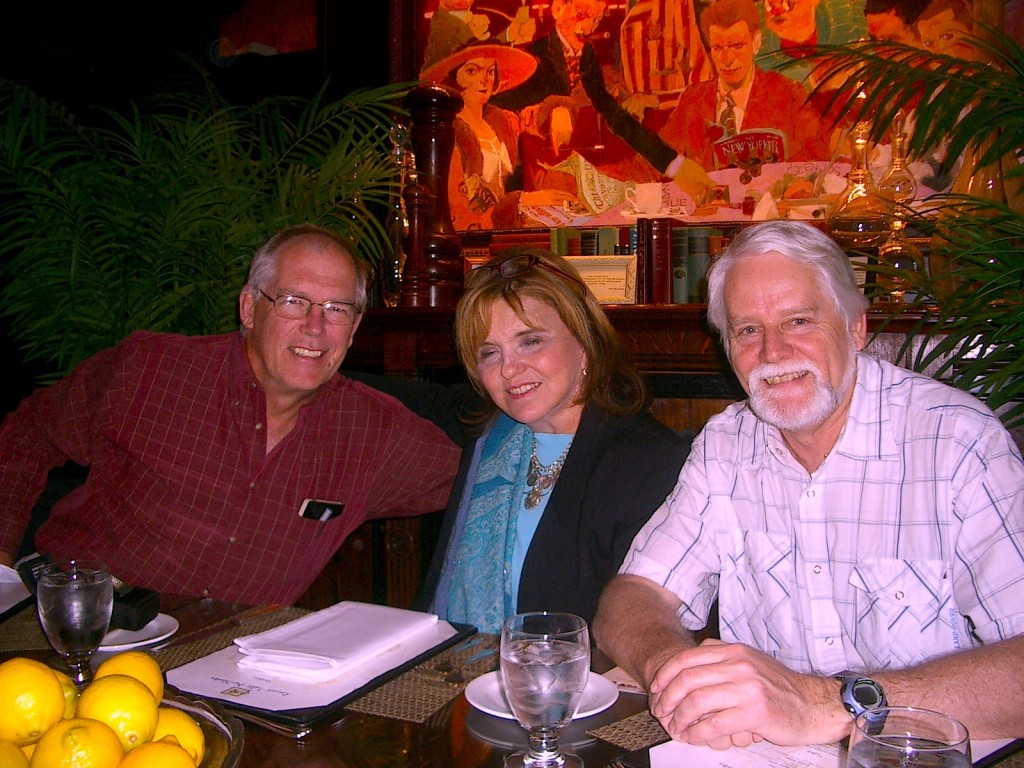

Stan (left) and Michael at the round table with their agent, Marly Rusoff
To win a copy of Michael Stanley’s latest book, all you have to do is answer this question: where are Stan and Michael hobnobbing with their agent? (Hint: as public places in New York City go, it could hardly be more literary.)
Answers should be emailed to michaelstanley@detectivekubu.com with subject line “Author! Author! contest” before September 15th. Three lucky winners will be drawn randomly from all correct answerers shortly thereafter, and the results shall be announced here and on the Detective Kubu website.
So this is a chance for fame as well as (modest) fortune!
Okay, now on to the technofest. As it happens, it directly relates to what you might be winning.
HarperCollins is beta-testing a nifty promotional feature that not only enables potential readers to browse books on its website, but allows me to offer my readers that opportunity, too. It’s not the whole book, mind you, and it’s not printable, but this feature does allow you to see more than most readers skim in a bookstore before buying. Take a gander, and see what you think:
What do you think? Like it as a promotional device, or would you rather be turning pages in a brick-and-mortar bookstore? Would you feel differently about it if it were your book being promoted this way — in other words, do you prefer it as a writer than as a reader, or vice-versa?
As if all that weren’t exciting enough for one post, we haven’t yet gotten to the watermelon at the heart of the cornucopia (oh, you had a better metaphor in mind?): Stan’s promised insights into the mysteries of book tours, working with publicists, and every author’s nightmare, what happens if no one shows up to a book signing.
So please join me in a big Author! Author! welcome for Stan Trollip! Take it away, Stan!





June 2nd saw the launch of our second Detective Kubu mystery — The Second Death of Goodluck Tinubu — at the wonderful Once Upon a Crime bookstore in Minneapolis, and kicked off something of a whirlwind book tour of the US. We visited 12 cities and 20 bookstores over about six weeks, but most of the trip was concentrated over a three-week period. During that time, we were in New York, Minneapolis, Urbana-Champaign IL, Chicago, Milwaukee, Detroit, Ann Arbor, Houston, San Diego, and Los Angeles. Book signings were interspersed with radio and TV slots and online interviews, and surrounded by Book Expo, Thrillerfest, and the American Library Association convention.
We were fortunate to have strong support from HarperCollins, particularly from our in-house publicist Heather Drucker, and things went smoothly as a result. And external publicist Susan Schwartzman buzzed around getting media slots for us. It would be a big challenge to arrange this sort of tour without the support of such knowledgeable and energetic people.

Michael with HarperCollins publicist Heather Drucker in New York City
Many writers don’t understand the role of the publicist at a major house. So here is how we see it. Several months before the book is released, the in-house publicist sends out review copies of the book to influential reviewers in the various media. This list is often compiled in collaboration with the authors, who may have insights into niche areas. If you have a publisher like HarperCollins, this can amount to well over a hundred books.
Then the publicist works with the authors to map out a book-tour itinerary. The extent of this depends on the publisher’s budget, which was zero for our first book, A Carrion Death, and small but significant for the second book, as well as how much the author is willing to contribute. For both books, we chipped in a sizeable amount of our advance to fund our tours.
Then the publicist contacts the bookstores or other organizations, such as libraries, and coordinates everything with them, including providing publicity materials if available, ensuring they have enough books to sell, helping to publicize the event, and so on. The publicist also coordinates the travel and accommodation arrangements. We try to stay with friends whenever possible, not only because it reduces costs, but is also much more fun.
Finally, the in-house publicist works with the external publicist to ensure that their efforts are coordinated. For example, Heather from HarperCollins worked with Susan (an external publicist whom we hired) to support her efforts to find radio and TV spots. She did this by supplying additional review copies of the book, providing book reviews as they came out, and coordinating the sale of books if appropriate.
We have heard stories of the in-house and external publicists competing. This is not a good situation! Before you hire an external publicist, you should coordinate with your in-house publicist so that you are building a team not a pair of competitors. In our case, Heather and Susan worked together wonderfully.
So what is our perspective on our book tour, looking back two months later?

Michael and Stanley answering questions at Once Upon A Crime
From the moment we launched The Second Death of Goodluck Tinubu, it was great fun. We talked to people who enjoy our books and had read both or intended to do so. We met booksellers who care about mystery books and have an intimidating knowledge of them and their authors. And we spent a lot of time together, enjoying the travel, sharing the experiences, and talking about our third book.
Second, we learned a lot. We discovered that people really care about the ongoing characters in the book, particularly our protagonist, Botswana police detective David Bengu (known as Kubu) and his family. Interestingly, few questions or comments related to Kubu himself, other than whether he was based on a real person (he isn’t). Perhaps people have already formed their own mental pictures of him and where he is going.
Readers really like his wife Joy and wonder what is happening with the relationship between Joy’s sister, Pleasant, and an occasional suitor, Bongani. We also heard a lot of positive comments about Kubu’s aging parents (Wilmon and Amantle). We were told they added to an understanding of the Botswana culture. This was very satisfying as we had decided early on in our writing to purposefully deal with the physical and cultural attributes of Botswana. We realized that doing so would slow the pace of the mystery a little, but hoped what it added would compensate. Our tour and the reviews we have received tell us that most readers like the style.

Michael and Stanley being pleased at readers’ reactions to A Carrion Death
Third, the tour was hard work. We did the Midwest, travelling by car from Chicago; there are long distances involved and the June weather was — to be polite — variable. We had plenty of good dinners with old friends, who turned out across the country to support us, but we had a few twists and turns along the way. One pit-stop restaurant we could only find sugared pop, other than tap water, and fried food. We were caught up in a demonstration in Los Angeles urging democracy in Iran. We were becalmed on the LA freeway. We had sessions with standing room only, and an event to which no one showed up.
We suspect that it is every writer’s nightmare to stand expectantly at the front of a room, and wait, and wait. Look at your watch. How long should we wait? Fifteen minutes? Thirty minutes. Feel embarrassed, awkward. Not sure what to say to the bookstore manager. She’s not sure what to say to you. It happened to us on a Sunday lunchtime on the city’s first nice summer day of the year. “Sundays are always busy,” she told us apologetically. But the first sight of the sun tempted even the most ardent readers and every chair was vacant.
In some ways, we were quite pleased it happened. We had got it out of the way — the nagging fear of an empty room. More importantly, we survived! And our egos were still intact. People on the street didn’t point at us surreptitiously and snigger. And it gave us something to write about in this blog.
All we can say is that it is going to happen. We are lucky to tour together, so at least we have each other to talk to. And maybe there is a lesson to be learned. Perhaps new authors should consider doing events in tandem with another author. At least then, when there is no audience, you have a companion with whom to share the disappointment.

Stan making the most of a book signing
At a more practical level, one can ask what these book tours achieve. Certainly we find it of value to learn in person what readers think and feel about our writing, even though we get similar feedback by email and over our website. We think the readers enjoy the events and find them interesting. In addition, bookstore owners and managers now have a personal experience of us to link to the books when they sell them.
But our feeling is that this sort of discussion is irrelevant for most people in the publishing industry, especially in the current weak economic environment. Their question would be: does the time and money spent on a book tour improve book sales?
It’s a difficult question to answer. One publicist told us that they know that only half of their marketing has any impact on sales — they just don’t know which half.
The same goes for us. We are both scientists and have a constant discomfort that there are no data about the effectiveness of what we do for publicity. In reality, we believe that book tours and so on are valuable, but don’t ask us to prove it.
Then there is the 90:10 rule – ninety percent of the marketing budget goes on the ten percent of authors who are best known, best sellers, and who need marketing the least. Since we are not in that ten percent, we are grateful for the slice we got of the other ten percent. We work hard and spend a considerable amount of our advances on marketing and touring. It is reassuring that HarperCollins is willing to support us in this.
Book tours outside North America seem to be uncommon except for well-known authors. We have done no more than a few signings in other countries. Declining to organize a function in Johannesburg for our second book, our South African publicist told us that launches don’t sell books; publicity sells books. We pointed out that the launch of A Carrion Death in Johannesburg sold over a hundred copies and attracted at least twice that number of people. Her response was: “Yes, it was an excellent launch. You have a lot of friends in Johannesburg.” So we threw our own party to which 100 or so people came, and we sold seventy books.
Would the same number of books have been sold anyway? We don’t know.
So how would we sum up our feelings about the book tour? Let’s put it this way. If we’re asked to do one next year for our third book, we’ll dip into our pockets and start buying the plane tickets.



 Michael Stanley is the writing team of Michael Sears and Stanley Trollip.
Michael Stanley is the writing team of Michael Sears and Stanley Trollip.
Both are retired professors who have worked in academia and business. They were both born in South Africa. Michael is a mathematician, specializing in geological remote sensing. He lives in Johannesburg, South Africa, and is a tournament bridge player. Stanley is an educational psychologist, specializing in the application of computers to teaching and learning, and a pilot. He splits his time between Knysna, South Africa, and Minneapolis in the United States. He is an avid golfer.
Their first novel, A CARRION DEATH, featuring Detective David “Kubu” Bengu, was published in 2008 and received critical acclaim. The Los Angeles Times listed it as one of its top ten crime novels of 2008. It is a nominee for the Minnesota Book Award, Strand Magazine’s Critics Award for Best First Novel, and Mystery Readers International Macavity Award for Best First Novel.

 (1) As with the keynote and the elevator speech, most pitchers make the mistake of trying to turn the pitch proper into a summary of the book’s plot.
(1) As with the keynote and the elevator speech, most pitchers make the mistake of trying to turn the pitch proper into a summary of the book’s plot. (2) Most pitchers don’t stop talking when their pitches are done.
(2) Most pitchers don’t stop talking when their pitches are done. (3) The vast majority of conference pitchers neither prepare adequately nor practice enough.
(3) The vast majority of conference pitchers neither prepare adequately nor practice enough. (4) Most pitchers harbor an absurd prejudice in favor of memorizing their pitches, and thus do not bring a written copy with them into the pitch meeting.
(4) Most pitchers harbor an absurd prejudice in favor of memorizing their pitches, and thus do not bring a written copy with them into the pitch meeting. (5) Most pitchers don’t realize until they are actually in the meeting that part of what they are demonstrating in the 2-minute pitch is their acumen as a storyteller. If, indeed, they realize it at all.
(5) Most pitchers don’t realize until they are actually in the meeting that part of what they are demonstrating in the 2-minute pitch is their acumen as a storyteller. If, indeed, they realize it at all. (6) Few pitches capture the voice of the manuscript they ostensibly represent.
(6) Few pitches capture the voice of the manuscript they ostensibly represent.  (7) Very few pitches include intriguing, one-of-a-kind details.
(7) Very few pitches include intriguing, one-of-a-kind details.  (8) Most pitchers assume that a pitch-hearer will hear — and digest — every word they say, yet the combination of pitch fatigue and hectic pitch environments virtually guarantee that will not be the case.
(8) Most pitchers assume that a pitch-hearer will hear — and digest — every word they say, yet the combination of pitch fatigue and hectic pitch environments virtually guarantee that will not be the case. (9) Few pitchers are comfortable enough with their pitches not feel thrown off course by follow-up questions.
(9) Few pitchers are comfortable enough with their pitches not feel thrown off course by follow-up questions. (10) Far too many pitchers labor under the false impression that if an agent or editor likes a pitch, s/he will snap up the book on the spot. In reality, they’re going to want to read the manuscript first.
(10) Far too many pitchers labor under the false impression that if an agent or editor likes a pitch, s/he will snap up the book on the spot. In reality, they’re going to want to read the manuscript first. If the agent is interested by your pitch, she will hand you her business card and ask you to send some portion of the manuscript — usually, the first chapter, the first 50 pages, or for nonfiction, the book proposal. If she’s very, very enthused, she may ask you to mail the whole thing.
If the agent is interested by your pitch, she will hand you her business card and ask you to send some portion of the manuscript — usually, the first chapter, the first 50 pages, or for nonfiction, the book proposal. If she’s very, very enthused, she may ask you to mail the whole thing.


















 Richard Hooker’s M*A*S*H — rejected by 21 publishing houses. {“How many Army doctors could there possibly be?” they must have scoffed. “And who else would care?”)
Richard Hooker’s M*A*S*H — rejected by 21 publishing houses. {“How many Army doctors could there possibly be?” they must have scoffed. “And who else would care?”) Thor Heyerdahl’s KON-TIKI — rejected by 20 publishing houses. (Yes, THAT Kon-Tiki. “This might appeal to people who sail for pleasure, but can we afford a novel for the yacht-owning niche?”)
Thor Heyerdahl’s KON-TIKI — rejected by 20 publishing houses. (Yes, THAT Kon-Tiki. “This might appeal to people who sail for pleasure, but can we afford a novel for the yacht-owning niche?”) Dr. Seuss’ first book, AND TO THINK THAT I SAW IT ON MULBERRY STREET — rejected by 23 publishing houses. (“Do we really want to confuse children?”)
Dr. Seuss’ first book, AND TO THINK THAT I SAW IT ON MULBERRY STREET — rejected by 23 publishing houses. (“Do we really want to confuse children?”) Richard Bach’s JONATHAN LIVINGSTON SEAGULL — rejected by 18 publishing houses. (“The only person I have ever known who cared about seagulls was my mad great-aunt Kate, who spent her last years wandering down to the beach to offer them caviar on crackers. Next!”)
Richard Bach’s JONATHAN LIVINGSTON SEAGULL — rejected by 18 publishing houses. (“The only person I have ever known who cared about seagulls was my mad great-aunt Kate, who spent her last years wandering down to the beach to offer them caviar on crackers. Next!”) Patrick Dennis’ AUNTIE MAME — rejected by 17 publishing houses. (I have no idea what they were thinking here; perhaps that it was really a memoir?)
Patrick Dennis’ AUNTIE MAME — rejected by 17 publishing houses. (I have no idea what they were thinking here; perhaps that it was really a memoir?)

























