Hello, campers –
Okay, I am officially annoyed: someone has had the temerity to write a bad Amazon review of my memoir, A FAMILY DARKLY: LOVE, LOSS, AND THE FINAL PASSIONS OF PHILIP K. DICK. Which would be a little less odd if the book had ever been released, but as far as I know, not even review copies were ever available.
And I certainly never sent this person a copy of any draft of my manuscript. So what can she possibly be reviewing? The blurb on the Amazon page — which, like pretty much every marketing blurb, was written not by the book’s author, but by the publisher’s marketing department?
Yes, yes, I know: Amazon lists my book as being out of print — limited ability, not as still to be released, which implies that there are a few copies running around out there. Their assertion is technically true, because it was never IN print, but factually inaccurate.
So how did it end up with a listing on Amazon at all? Well, as long-time readers of this blog already know, Carroll & Graf was supposed to publish it in February, 2006 — then May, 2006, then September, 2006 — before the project was permanently put on ice, due to a series of nebulous threats from the Dick estate. Although to the best of my knowledge, they never asked my publisher to make any changes in the book whatsoever, the figure two million dollars was bandied about menacingly.
A right about the same time as the A MILLION LITTLE PIECES scandal broke. That the publisher would balk was inevitable.
I’ve come to peace with all that, mostly: I have faith that the book will eventually come out, even if I have to outlive the naysayers to do it; it’s not as though the audience for it is going to disappear. I know that my memoir is honest; someday, a larger audience will see the story.
In the meantime, I have a life to live and books to write.
Still, it rankles me that someone who apparently hasn’t read the book should review it — and that the review should have come (evidently) from one of Philip’s ex-wives — to be precise, the one three wives after my mother. I don’t even understand why Amazon would ALLOW her to review it, when for over two years now, it apparently hasn’t permitted others who HAVE read drafts of the book to post reviews.
You HAVE already lined up fellow writers to tap out Amazon reviews for you when your first book comes out, right?
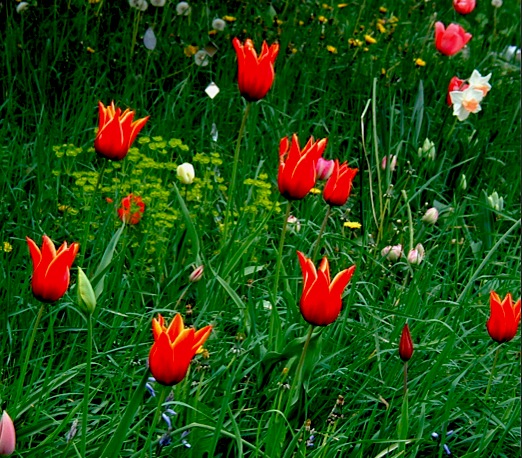
What makes me think that this review didn’t filch a stray draft copy to pass judgment upon, you ask? Because her sole stated objection to the book is that I couldn’t possibly have spoken with Philip on the telephone, because, she claims — brace yourselves, because I think this is going to come as a shocker to those hoping to make a career writing science fiction — she and Philip were too poor to afford a phone during their very brief marriage.
Interesting claim. She is presumably referring to the early 70s, when Philip had been publishing his writing successfully for over 15 years, including a little number called THE MAN IN THE HIGH CASTLE. It won a Hugo Award in 1963, not an achievement typically associated with a writer’s book sales declining to the point of penury, especially one as prolific as Philip was throughout the 1960s.
But even he had been reduced to living in a treehouse in a public park, my memoir isn’t ABOUT the early 70s, as those happy few who have read the manuscript could tell you. It takes place mostly in the late 70s and early 80s, when Philip and I were indeed talking on the phone a great deal (as were others, some of whom seem to recall having picked up the phone a few years earlier and calling…well, never mind), and the 1950s, when Philip and my mother were married. (The same period when, not entirely coincidentally, he was working with my father, my science fiction-writer uncle was giving him marketing advice, and my godfather was dropping by to play chess…well, you get the picture.)
In other words, I’ve been writing what I know.
In fact, for this critique to be remotely apt, my entire memoir would have to have been devoted to ages 5 to 8 — years which, if memory serves, take up only a small handful of pages in the manuscript at all. Why? Well, I was a precocious child, certainly, but if I was slandering anyone mid-elementary school, it’s news to me.
Even if there were an honest difference of recollection here (which I don’t think is the case), why this review should wait to bring this up until more than two years after the book in question was supposed to be released mystifies me. Unless she’s planning to write a book of her own?
And don’t even get me started on the irony of someone who has ever been married to an SF/fantasy writer using the term fantasy as an insult about a piece of writing.
Okay — deep breath. I don’t need to get upset over this. But I have to tell you, it did give me a turn to be accused of slander on an Amazon discussion board. (In an apparent effort to leave no stone unturned in discrediting me, the reviewer evidently started a discussion thread. Thorough of her, no?)
Now, to set all of you memoirists’ minds at ease, this is a pretty empty accusation — the dead have no reputations, my lawyer tells me, and thus cannot be libeled. Also, rumor has it that truth is an absolute defense against both libel and slander, and so far, no one who has objected to the book’s publication has shown me — or, to the best of my knowledge, my publisher — any evidence whatseverthat my memories are not grounded in fact. It’s all just been assertions of different points of view.
Which, strange to say, has been hard to get the relevant parties to understand. Contrary to criticisms leveled at some popular memoirists lately, few people’s lives are documented down to the last second. How would you, for instance, prove that everything that happened on your first date actually occurred, in the absence of the other party?
You couldn’t, of course. Welcome to the dilemma of the present-day memoirist.
I can’t even begin to tell you how tired I am of all this — I’ve been defending this book for over three years now, without anyone ever having produced a single tangible reason it shouldn’t be published. Yet until today, as far as I knew, no one had ever even implied that anything about my memoir had broken the law.
Prior to this review, the issues of alternate points of view and who owns personal memories, if not the person herself — both subjects upon which Philip Dick wrote frequently, as it happens — dominated the discussion of my memoir. Now, it seems as though my very memories are being called libelous.
I can’t explain it.
In fact, I wouldn’t be bringing it up at all, except the only reason I found out about this puzzling review at all was that I was double-checking a link in the post below, a little gem on standard format from last December. To be precise, I originally posted it on Philip’s birthday.
Don’t ever say I didn’t do anything for you people; I may never double-check a link again. Enjoy the post.
Many thanks to all of you sweet souls who forwarded me links to the many literary and SF sites out there that commemorated what would have been my good old friend Philip K. Dick’s 79th birthday. This was the first year that I received a whole boatload of these messages, so it was great fun — rather like receiving a flotilla of birthday cards in the mail.
I needed the cheering up, I’m afraid, as usually, I throw a little dinner party on this particular day. Not only out of respect for my first serious writing teacher, but also as a birthday shindig for some of the other great artists born today: Beethoven, Sir Noël Coward, Sir Arthur C. Clarke (of 2001 and CHILDHOOD’S END fame), and of course, Author! Author!’s own beloved, wise auntie, Jane Austen.
You could do worse than to raise a glass to that crowd. But this year, I’ve just been too wiped out to allow anyone but the postman to drop by — and some days, I’m not even up to seeing him.
Thus, no dinner party this year, more’s the pity. I did a little too much last week, so this weekend, all I did was sleep and make groggy suggestions about how to maneuver the Christmas tree in order to make it stand up straight. (Which actually is necessary in our household: due to a truly spectacular bracken-and-cat interaction a few years back, we now tie the top of the tree to a ring firmly attached to the ceiling, so the tree does not need to be completely vertical in order to keep from toppling over.)
But enough about me; let’s talk about you.
While I was incapacitated, a group of my wonderful readers was holding down the fort here, trading tips on how to deal with that pesky problem, how to add a second space between sentences if a writer had mistakenly typed the whole thing thinking there should only be one. If you have even a passing interest in this topic, I implore you, check out the comments on the last two days’ posts; it’s well worth it. (Here’s a link to the first and here’s one to the second.)
We have only few rules of standard format left to cover in this series, so my first instinct was to use the text of one of Philip’s short stories for the examples. (Seemed appropriate, given that he used to mark deviations from standard format on stories I wrote for school and send them back to me for correction. What 11-year-old girl wouldn’t have loved THAT?) But since fair use permits only 50 consecutive words in a quote without explicit permission from the copyright holder, and the copyright holders in his case have a nasty habit of waving $2 million lawsuits in my general direction (and my quondam publisher’s) every time I so much as breathe his name, that didn’t seem entirely wise.
So I thought, in honor of the day, I would use a little something that I am undoubtedly entitled to reproduce here. Here is the first page of Chapter Six of my memoir:
Every chapter should begin like this: on a fresh page, 12 single lines (or 6 double-spaced) from the top.
As with the first page of text, the only reference to the author’s name or the title should appear in the slug line, located in the upper left-hand margin. (And in answer to reader Janet’s intelligent question: the slug line should appear .5 inches from the top of the paper, floating within the 1-inch-deep top margin. I can’t believe I never mentioned that before.) The page number belongs within it, rather than anywhere else on the page.
The slug line confuses a lot of aspiring writers; until you have seen piles and piles of professional manuscripts, it looks kind of funny, doesn’t it? And when you’ve been told over and over again that a manuscript should have a 1-inch margin on all sides, it can seem counterintuitive to add a line of text, even such a short one, IN that margin.
But I assure you, it’s always been done that way. And why? Followers of this series, chant it with me now: BECAUSE IT LOOKS RIGHT.
Yes, that logic IS tautological, now that you mention it. If you have a problem with that, I would suggest taking it up with the powers that rule the universe. I, as I believe the reference above to my memoir’s troubled path makes abundantly clear, apparently do not rule the universe.
If I did, today would be a holiday for every writer on the planet. Especially the ones who are having trouble getting their work published, like, oh, Philip K. Dick, Arthur C. Clarke, and Jane Austen all did at the beginning of their fiction careers.
I just mention.
Back to business. Placing the slug line in the header (located in Word under the VIEW menu) also enables the writer to take advantage of one of the true boons of the advent of word processing, pages that number themselves. Every so often, I will receive a manuscript where the author has, with obviously monumental effort, typed a slug line onto the first line of TEXT of each page, so it looks like this:
See how pulling the slug line down into the text messes with the spacing of the page? An entire line of text is sacrificed to it — and let me tell you, that line is not going to go quietly.
Why not? Well, what’s going to happen if new writing is inserted on a page formatted this way? That’s right: the author is going to have to go back and move each and every one of those slug lines to match the NEW pagination.
I’d show you a picture of this, but it’s just too ugly to contemplate. Trust me, it would be a heck of a lot of work.
See any other problems with this page? How about the fact that the slug line includes the word PAGE? Shouldn’t be there; just the numbers will suffice.
Did I just hear some huffs of indignation out there? “But Anne,” I hear the formatting-ambitious cry, “it’s kind of stylish to include PAGE before the page number, isn’t it? It’s just a matter of personal style — who could be hurt by including it, if I like the way it looks?”
Well, you, for starters. And why? (Chanters, ready your lungs.) BECAUSE IT JUST WOULD NOT LOOK RIGHT TO A PROFESSIONAL READER.
I’m quite serious about this; I’ve seen screeners get quite huffy about this one. “Does this writer think I’m STUPID?” Millicent is prone to huff. (Don’t answer that question; it’s rhetorical.) “Does she think I DON’T know that the numeral that appears on every page refers to the number of pages? Does she think I’m going to go nuts and suddenly decide that it is a statistic, or part of the title?”
Don’t bait her. Do it the standard way.
Okay, did you spot any other problems? What about the fact that the first paragraph of the chapter is not indented, and the first character is in a different typeface?
The odd typeface for the first letter, in imitation of the illuminated texts hand-written by monks in the Middle Ages, doesn’t turn up all that often in manuscripts other than fantasy and YA, for one simple reason: books in that category are more likely to feature this it’s-a-new-chapter signal than others. But once again, what an editor may decide, rightly or wrongly, is appropriate for a published book has no bearing upon what Millicent expects to see in a manuscript.
Save the bells and whistles for someone who will appreciate them. Hop in your time machine and track down a medieval monk to admire your handiwork, if you like, but in this timeframe, keep the entire manuscript in the same typeface and size.
The non-indented first paragraph of a chapter is fairly common in mystery submissions, I have noticed. I’ve been told by many mystery writers that this is an homage to the great early writers in the genre, an echo of their style.
But you know what? Almost without exception, in Edgar Allan Poe’s time all the way down to our own, the EDITOR has determined the formatting that appeared on any given printed page, not the author. To professional eyes, especially peevish ones like Millicent’s, a manuscript that implicitly appropriates this sort of decision as authorial might as well be the first step to the writer’s marching into Random House, yanking off a well-worn riding glove, and striking the editor-in-chief with it.
Yes, you read that correctly: it’s sometimes seen as a challenge to editorial authority. And while we could speculate for the next week about the level of insecurity that would prompt regarding a minor formatting choice as a harbinger of incipient insurrection, is the manuscript of your first book REALLY the right place to engender that discussion?
Exactly.
If you want to make Millicent and her bosses happy — or, at any rate, to keep them reading calmly — indent every paragraph of the text should the expected five spaces. It just looks right that way.
While we’re at it, how about the bolded chapter number and title? Nothing in a manuscript should be in boldface. Nothing, I tell you. Uh-uh. Not ever.
Well, you could get away with the title itself on the tile page, but frankly, I wouldn’t chance it.
Nor should anything be underlined — not even names of books or song titles. Instead, they should be italicized, as should words in foreign tongues that are not proper nouns.
I heard that gigantic intake of breath out there from those of you who remember constructing manuscripts on typewriters: yes, Virginia, back in the day, underlining WAS the norm, for the simple reason that most typewriters did not have italic keys.
If you consult an older list of formatting restrictions, you might conceivably be told that publications, song titles, and/or foreign words (sacre bleu!) should be underlined. But trust me on this one: any agent would tell you to get rid of the underlining, pronto.
And why? All together now: because IT JUST DOESN’T LOOK RIGHT THAT WAY.
All right, campers, do you feel ready to fly solo? Here are two pages of text, studded with standard format violations for your ferreting-out pleasure. (I wrote these pages, too, in case anyone is worried about copyright violation or is thinking about suing me over it. Hey, stranger things have happened.)
How did you do? Are those problems just leaping off the page at you now? To reward you for so much hard work, here are a couple of correctly-formatted pages, to soothe your tired eyes:

Whenever you start finding yourself chafing at the rules of standard format, come back and take a side-by-side gander at these last sets of examples — because, I assure you, after a professional reader like Millicent has been at it even a fairly short time, every time she sees the bad example, mentally, she’s picturing the good example right next to it.
And you know what? Manuscripts that look right get taken more seriously than those that don’t. And regardless of how you may feel about Millicent’s literary tastes, isn’t a serious read from her what you want for your book?
Keep up the good work!